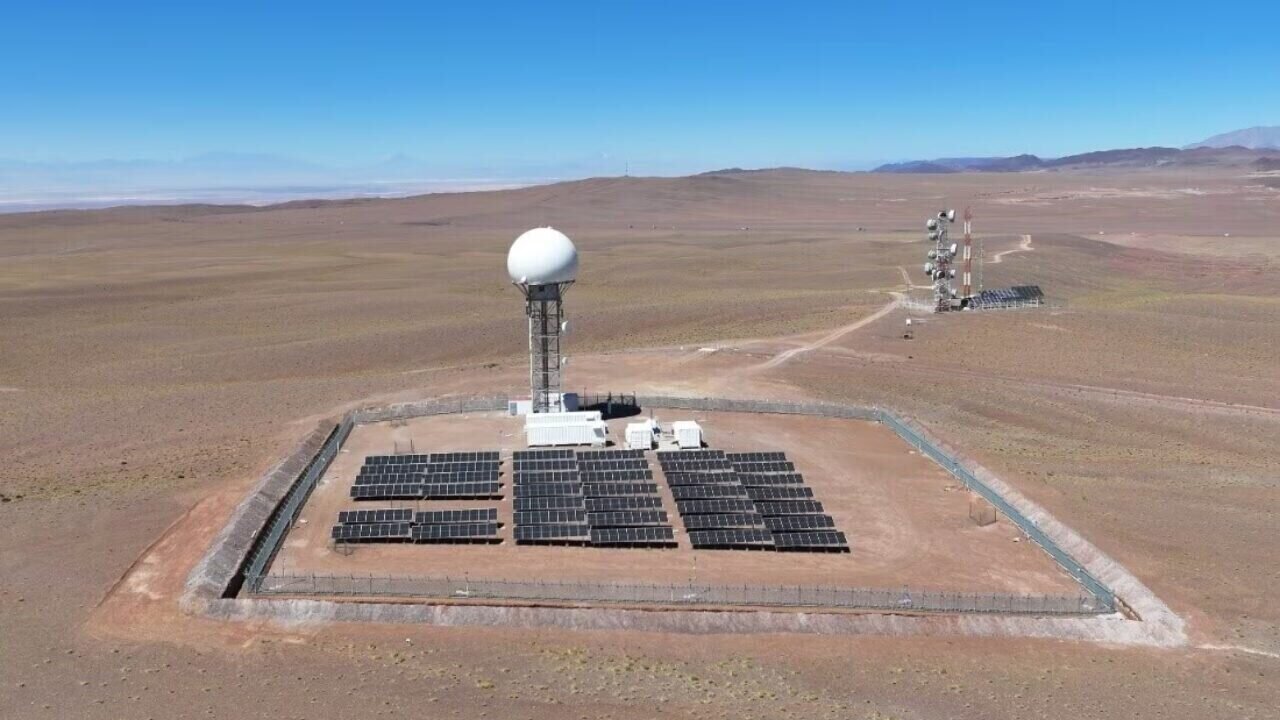
Chile’s General Directorate of Civil Aeronautics (DGAC) and Thales are operating the world’s first 100% powered by solar energy air traffic control radar station.
It is said that this technological innovation places Chile at the forefront of sustainable initiatives within the civil aviation industry for a greener future and ensures secure air traffic surveillance in Northern Chile.
Developed by Thales for the Dirección General de Aeronáutica Civil (DGAC), the solar-powered radar system is comprised of an advanced and efficient STAR NG primary radar and RSM secondary radar. Combined, the radars provide all the operational surveillance requirements of both civil and military air traffic control detecting both slow and fast-moving targets such as helicopters, commercial planes, and jets.
Thales made the following statement on the solar-powered radar station:
“The 100% solar paneled ATC radar station will help monitor the commercial flights operated daily by the DGAC in the country, providing increased safety and reliability.
Located in the Atacama Desert in Northern Chile at more than 3500 meters, the radar station will run exclusively on sustainable energy by harnessing the region's high solar incidence. Equipped with 340 strategically positioned panels, the station has a maximum generation capacity of approximately 960 kWh per day, covering an area of 10,000 m2.
Launched one year ago, the innovation in terms of alternate and greener power generation is an example of Thales’ role as a strategic partner, with engineers and technology being at the forefront to deliver sustainable solutions in all environments. In addition to the solar panels, the system includes efficient energy use and advanced battery and backup generator technology to ensure the overall operation of the station.”
“For DGAC, at a strategic level, this new air traffic control radar station is undoubtedly a great contribution to air safety in the north of the country where there is currently a high air traffic density that will be fully covered by this new system, given its measurement range, which is the highest in the market at 100 nautical miles in the case of the primary radar and 250 nautical miles in the case of the secondary radar. The environment benefits are also outstanding and unique, limiting its impact on climate change by being 100% powered by solar energy which is consistent with the Chilean policies and the ones adopted by ICAO, in line with the concept that all nations should spare no effort to mitigate and reduce the environmental impact so that the next generations and our planet have a more sustainable future.” said Juan Alegría, Systems Director DGAC
“This project delivery is a milestone in the civil aviation industry and a commitment to sustainability. This is not only a technological achievement for DGAC and Thales, but also an example of environmental responsibility, demonstrating Thales’ commitment and capability to create sustainable solutions in-line with customer sustainable requirements and global objectives of preserving the environment. It is an example of a project contributing to low carbon future and contributes to the IATA to Fly Net Zero by 2050 commitment. It demonstrates how Thales advanced technologies are helping to make the world safer and more environmentally responsible.” said Lionel de Castellane, VP Civil radars segment, Thales